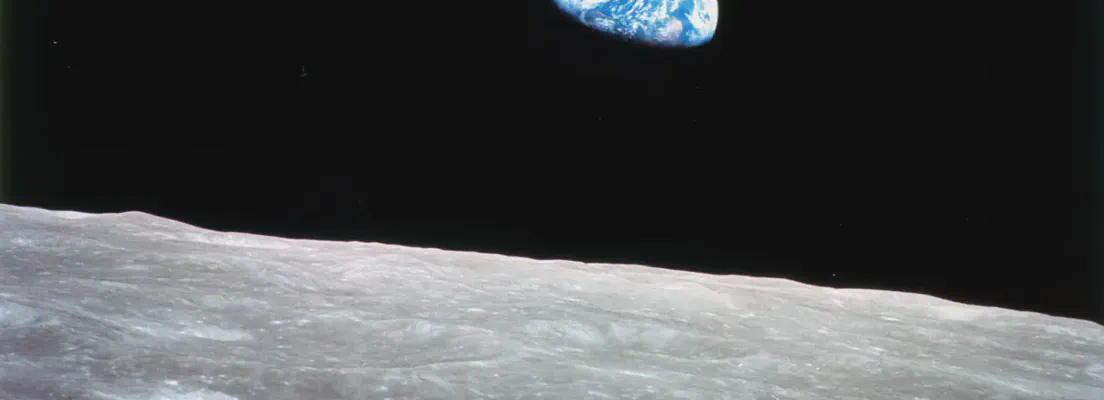
Space exploration has been a fascination for many of us for centuries. With the advent of space travel, more and more people have been exploring the mysteries of the universe. But it all begins with astronomy, the study of the stars, planets, and other objects in space. In this blog article, we’ll discuss astronomy and space knowledge in detail.

— Abed Ismail
What is Astronomy?
Astronomy is the scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, comets, nebulae, galaxies, and phenomena that originate outside the Earth’s atmosphere. The field of astronomy includes a wide range of topics, from studying the birth and death of stars to the formation of galaxies to the structure and evolution of the universe. Astronomy is also concerned with the study of the properties and motion of objects in space, and how they interact with each other.
Astronomers also use the tools of mathematics and physics to understand the behavior of these objects. For example, they use equations to describe the motion of planets and stars, and they use models to simulate the formation of galaxies and other structures in the universe. Astronomers also use telescopes and other instruments to observe the objects they study.
Astronomy is an ancient science, since we know the Egyptians, Jews, Christians and Muslims, it depends on astronomy (i.e. moon, sun and seasons on earth) in determining the calendar, some astronomy studies and exploration are often inspired by ideas written in the Torah, Gospels and Quran.

— Pikiran Rakyat
Astronomy History

— K. Mitch Hodge
The scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries saw the development of modern astronomy, with the invention of the telescope and the discovery of planets around other stars. This led to a more systematic and scientific approach to the study of the heavens, which is still used today.
In the 19th century, the field of astrophysics was born, with the development of the laws of motion and gravity, and the discovery of the structure of the universe. This led to a more comprehensive understanding of the universe and its workings.
The 20th century saw a huge expansion in the study of astronomy, with the development of powerful telescopes and satellites, and more accurate instruments for observing the universe.
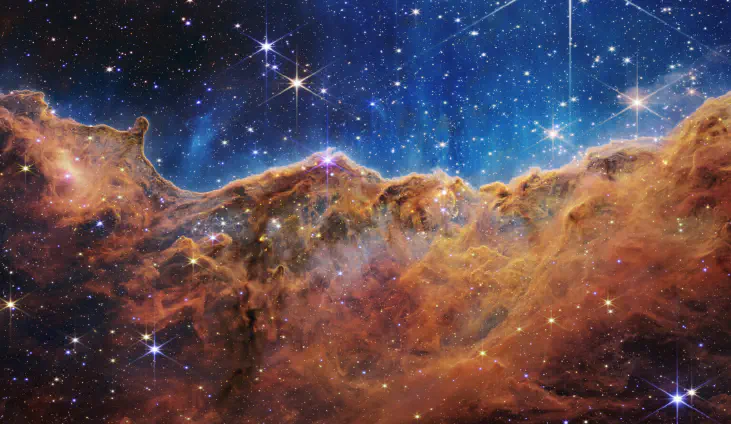

— NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI
For the example, The James Webb Space Telescope was launched on 25 December 2021 on an Ariane 5 rocket from Kourou, French Guiana, and arrived at the Sun–Earth L2 Lagrange point in January 2022. The first JWST image was released to the public via a press conference on 11 July 2022.
The History of Space Race
Some discoveries and progress, often emerged due to competition even because of conflict and war, as well as in the field of astronomy. After World War II drew to a close in the mid-20th century, a new conflict began. Known as the Cold War, this battle pitted the world’s two great powers, the democratic, capitalist United States and the communist Soviet Union, against each other.
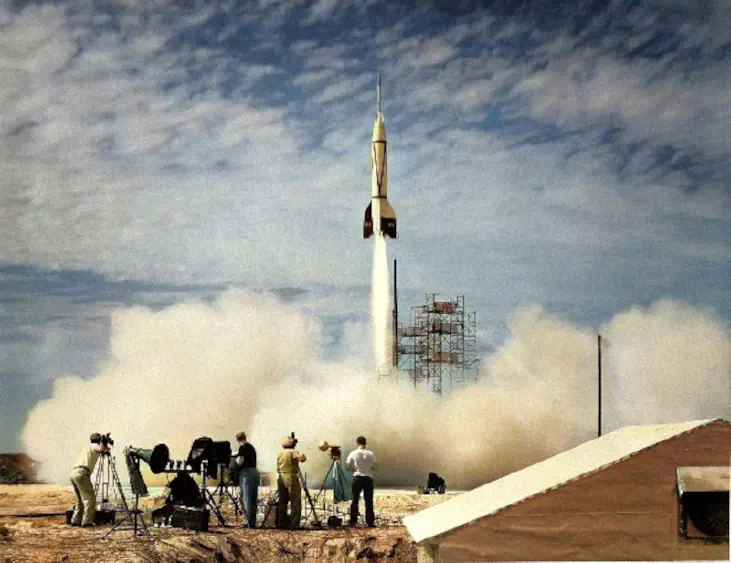

— Leonardo Times
By the mid-1950s, the U.S.-Soviet Cold War had worked its way into the fabric of everyday life in both countries, fueled by the arms race and the growing threat of nuclear weapons, wide-ranging espionage and counter-espionage between the two countries, war in Korea and a clash of words and ideas carried out in the media. These tensions would continue throughout the space race, exacerbated by such events as the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961, the Cuban missile crisis of 1962 and the outbreak of war in Southeast Asia.
Beginning in the late 1950s, space would become another dramatic arena for this competition, as each side sought to prove the superiority of its technology, its military firepower and–by extension–its political-economic system.
In 1958, the U.S. launched its own satellite, Explorer I, designed by the U.S. Army under the direction of rocket scientist Wernher von Braun (a German and American aerospace engineer and space architect). That same year, President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed a public order creating the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), a federal agency dedicated to space exploration.
Eisenhower also created two national security-oriented space programs that would operate simultaneously with NASA’s program. The first, spearheaded by the U.S. Air Force, dedicated itself to exploiting the military potential of space. The second, led by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), the Air Force and a new organization called the National Reconnaissance Office (kept classified until the early 1990s) was code-named Corona; it would use orbiting satellites to gather intelligence on the Soviet Union and its allies.
On July 16, 1969, U.S. astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin and Michael Collins set off on the Apollo 11 space mission, the first lunar landing attempt. After landing successfully on July 20, Armstrong became the first man to walk on the moon’s surface; he famously called the moment:
one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind
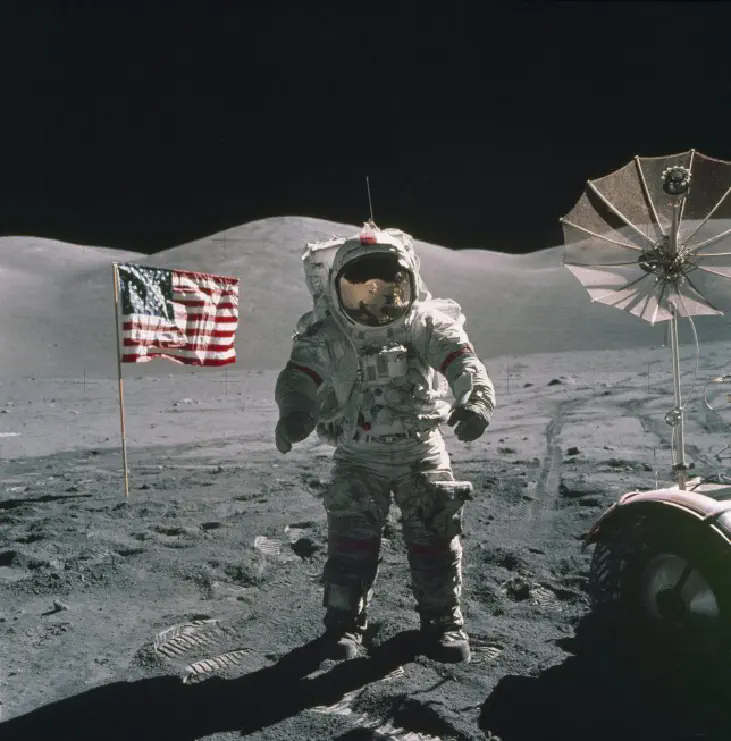

— NASA
By landing on the moon, the United States effectively “won” the space race that had begun with Sputnik’s launch in 1957. For their part, the Soviets made several failed attempts to launch a lunar landing craft between 1969 and 1972, including a spectacular launch-pad explosion in July 1969. [The Space Race]
The International Space Station (ISS)
In the next stage after the cold war ended, The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station in low Earth orbit was established. The project involves five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements.
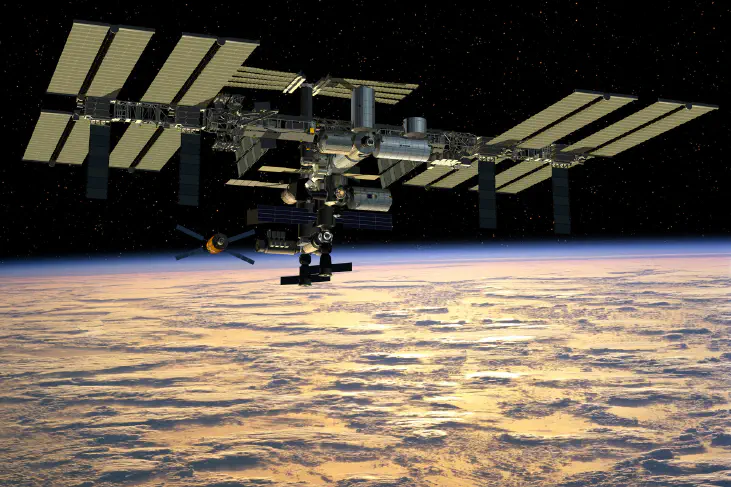

— NASA
The ISS simplifies individual experiments by allowing groups of experiments to share the same launches and crew time. Research is conducted in a wide variety of fields, including astrobiology, astronomy, physical sciences, materials science, space weather, meteorology, and human research including space medicine and the life sciences.
As of April 2022, 251 astronauts, cosmonauts, and space tourists from 20 different nations have visited the space station, many of them multiple times. [International Space Station]
Astronomy Facts
Astronomy is a fascinating science, and there are many interesting facts about space and the universe. Here are some of the most fascinating astronomy facts:
The universe is estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old.
The Milky Way galaxy, which contains our Earth, our Solar System, is estimated to contain between 200 and 400 billion stars.
The Sun is the closest star to Earth and is located about 93 million miles away.
There are an estimated 100 billion galaxies in the universe.
The Moon is the only natural satellite of Earth and is located about 238,900 miles away.
The planet Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and is located about 141 million miles away.
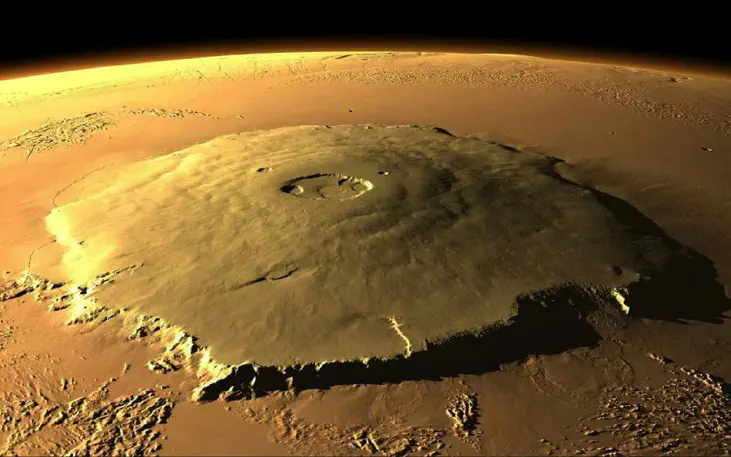

— NASA
The temperature of space is estimated to be around -455 degrees Fahrenheit.
The nearest black hole to Earth is located about 1,600 light-years away.
The universe is estimated to be expanding at a rate of about 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
The most distant galaxy ever observed is estimated to be about 13.3 billion light-years away.

— NASA
These facts demonstrate the immense scale of the universe and the wonders that can be found within it. You can find up more fascinating astronomy fact in your favorite search engine (e.g. Google, Yahoo, Bing and Duckduckgo) with keyword Astronomy Facts.
Types of Astronomy
Many different types of astronomy can be studied. The most common types are:
Observational astronomy: This type of astronomy involves observing objects in the sky through telescopes and other instruments. It is used to study the structure and motion of stars, galaxies, and other objects.
Theoretical astronomy: This type of astronomy involves using mathematical models to understand the behavior of objects in the universe. It is used to study the formation and evolution of galaxies, stars, and other objects.
Astrochemistry: This type of astronomy involves studying the composition of stars and other objects in the universe. It is used to study the formation and evolution of stars and galaxies.
Astrophysics: This type of astronomy involves studying the physical laws that govern the behavior of objects in the universe. It is used to study the structure and evolution of the universe.
Cosmology: This type of astronomy involves studying the origin and evolution of the universe. It is used to study the structure and evolution of the universe.
Astrobiology: This type of astronomy involves studying the possibility of life in the universe. It is used to study the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
These are just some of the types of astronomy that can be studied.
Space Exploration
Space exploration is the exploration of outer space using spacecraft and other robotic devices. Astronomy plays a vital role in space exploration, as it is used to study the planets, moons, asteroids, and other objects in space.

— NASA
Astronomers use telescopes and other instruments to observe these objects and learn more about them. This helps astronauts and other space travelers to plan their missions and navigate their spacecraft. Astronomers also use mathematical models to simulate the behavior of objects in space, so that space travelers can plan their missions more accurately.
Astronomy also plays a role in the search for extraterrestrial life. Astronomers use telescopes and other instruments to scan the skies for signs of life on other planets. This helps to answer one of the most fundamental questions in astronomy: Are we alone in the universe?
Space Research
Astronomy is also used in space research. Astronomers use telescopes, satellites, and other instruments to study the structure and evolution of stars, galaxies, and other objects in the universe. This helps to answer questions such as: How did the universe form? What is the nature of dark matter? What is the origin of galaxies?

— NASA
Astronomers also use mathematical models to simulate the behavior of objects in space and to test theories about the structure and evolution of the universe. This helps to answer questions such as: What is the nature of dark energy? What is the fate of the universe?
Astronomy is also used to study planets and moons in our Solar System, and to search for planets around other stars. This helps to answer questions such as: Are there other planets that could support life? Are there planets that could be habitable for humans?
Astronomy & Space Terminology
Astronomy has its special language, with many terms and phrases that are used to describe the objects and phenomena in the universe. Here are some of the more common terms used in astronomy:
Star: A bright, luminous object in the night sky, composed of gases and dust.
Planet: A large body that orbits a star, typically composed of rock and metal.
Galaxy: A large collection of stars, gas, and dust that is held together by gravity.
Nebula: A large cloud of gas and dust in space.
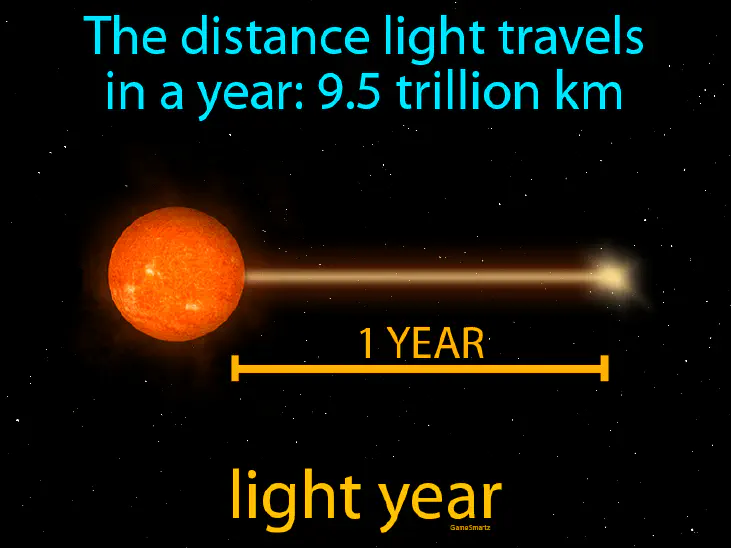
Light-year: The distance light travels in one year, which is about 9.5 trillion kilometers.
— Gamesmartz
Asteroid: A small rocky body that orbits the Sun.
Comet: A small body that is composed of ice, dust, and gas, and orbits the Sun.
Meteor: A small piece of rock or metal that enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns up.
Meteorite: A small piece of rock or metal that has survived its passage through Earth’s atmosphere and has landed on the ground.
Dark matter: An invisible form of matter that does not emit light, but is believed to make up the majority of the matter in the universe.
These are just some of the terms used in astronomy, but there are many more.
Space Technology
Astronomy relies heavily on technology to observe and study the objects in the universe. Telescopes are the most commonly used instruments in astronomy, as they allow us to observe distant objects in the night sky.
In recent years, powerful computers and advanced software have been developed to help astronomers simulate the behavior of objects in the universe. This has allowed astronomers to create detailed models of galaxies, stars, and other objects, and to answer many of the most fundamental questions in astronomy.
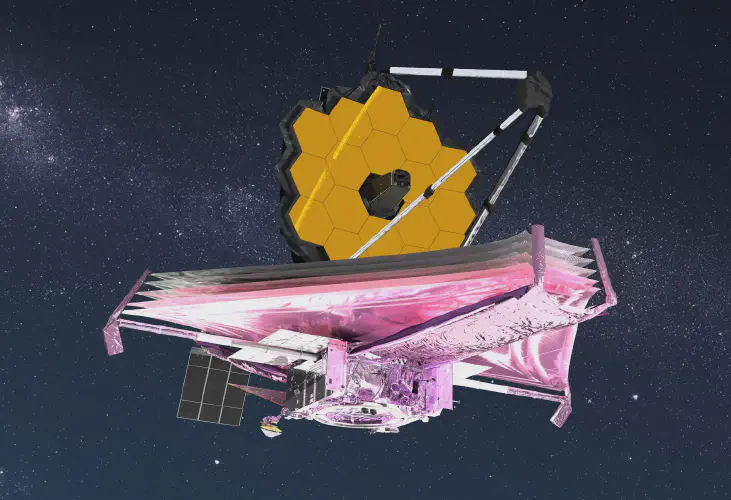

— ESA
Satellites and spacecraft have also been used to observe and study distant objects in space. These include the Hubble Space Telescope, which has revolutionized our understanding of the universe, and robotic probes like Voyager 1 and 2, which have sent back detailed images of the outer planets.
Astronomy Education
Astronomy is an important subject in science education, as it helps to introduce students to the wonders of the universe. Astronomy can be taught in a variety of ways, from classroom lectures to field trips to observatories.

— AstroFacts
Many schools also offer astronomy clubs and other activities to help students learn more about the universe. These clubs often organize visits to observatories and planetariums, and host lectures and astronomy discussions.
Astronomy is also an important part of science fairs and other competitions. Students can participate in projects that involve using telescopes and other instruments to observe the night sky, or creating models of planets and other objects. These projects can help to spark a lifelong interest in astronomy.
Thus a quick of view of astronomy and space knowledge. I hope this article has helped to give you some insight into astronomy and space knowledge.
As you can see, space exploration and astronomy are related fields, and both rely heavily on each other. Astronomy helps us to understand the structure and evolution of the universe, while space exploration helps us to explore the mysteries of the universe.
By understanding astronomy and space knowledge, we can gain a better appreciation of the universe and its many wonders. So let’s keep exploring the stars and discovering new things about the universe!



